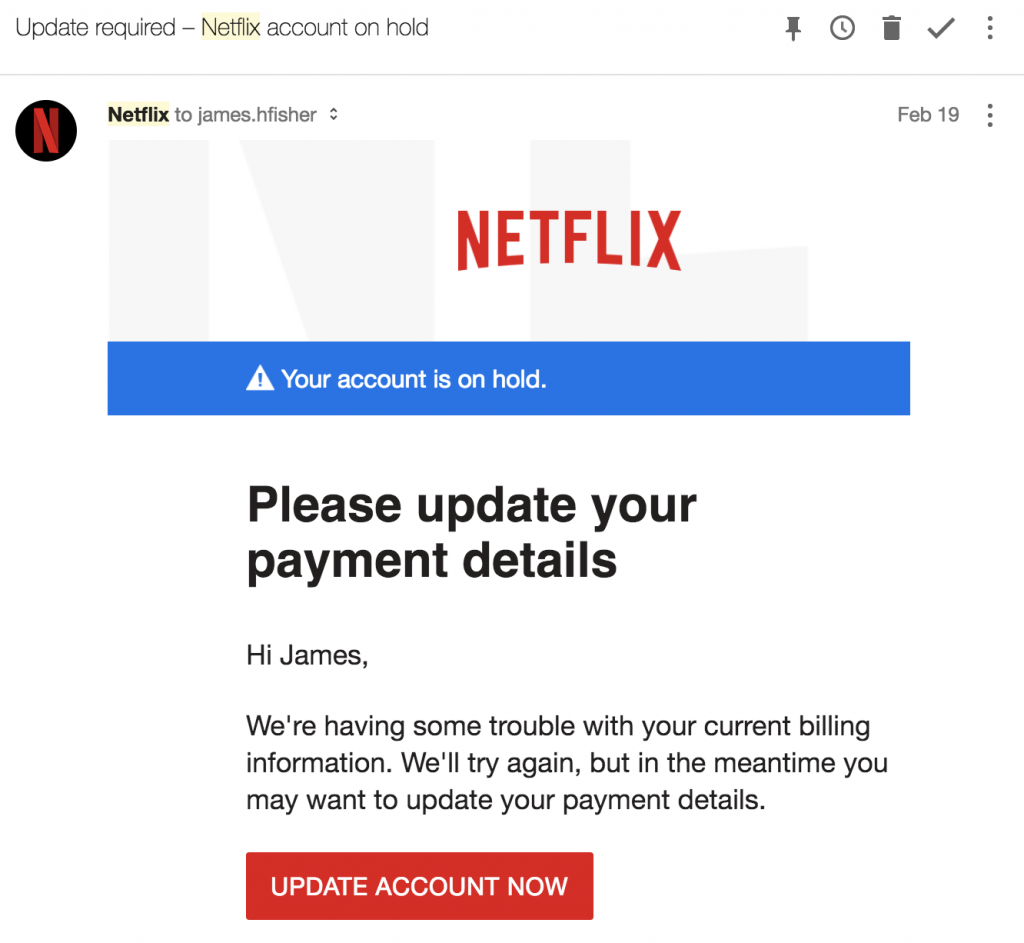
Users who don’t undergo cyber awareness training fail phishing tests.
Nearly all malware is delivered by email.
Of organisations have experienced a phishing attack in the past year
Did anything look out of the ordinary?
Did you recognize the senders address?
Was it similar but not the same as an official email?
If you ever think that an email is suspicious it is better to err on the side of caution.
Forward it to support@navada.com.au